Facing a dead car battery can be frustrating, but knowing how to charge it yourself in your car is a valuable skill. This guide will walk you through the essential tools, crucial safety precautions, and a clear, step-by-step process for connecting a charger and safely bringing your battery back to life. You’ll learn how to charge car battery in car effectively, ensuring you’re prepared for unexpected power loss and keeping your vehicle reliable.
There’s nothing quite like the sinking feeling you get when you turn the key in the ignition, and instead of a powerful roar, you’re met with a weak click, or worse, absolute silence. A dead car battery is one of the most common and inconvenient automotive problems drivers face. It often strikes at the worst possible time – when you’re late for work, rushing to an appointment, or stranded in a parking lot far from home. While jumping a car is a common solution, sometimes you need a more thorough charge, especially if your battery is deeply discharged or has been sitting for a while. That’s where knowing how to charge car battery in car comes in incredibly handy.
You might be thinking, “Can I really charge my car battery while it’s still in the car?” The answer is a resounding yes! With the right tools, a bit of know-how, and a strong emphasis on safety, you can effectively revive your car’s power source without removing it. This not only saves you the hassle of lugging a heavy battery around but also ensures you maintain all your vehicle’s electronic settings.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about how to charge car battery in car. We’ll cover the different types of chargers, crucial safety precautions, a clear step-by-step process for connecting and charging, and even tips for maintaining your battery to prevent future woes. By the end of this article, you’ll feel confident tackling a dead battery and keeping your vehicle reliably powered, no matter the situation.
Key Takeaways
- Safety First: Always prioritize personal safety by wearing protective gear and ensuring proper ventilation in your work area.
- Understand Your Battery: Know your battery type (e.g., Lead-Acid, AGM) and common reasons for discharge to prevent future issues.
- Choose the Right Charger: Use a smart (automatic) charger or battery maintainer for optimal and safe charging, especially when learning how to charge car battery in car.
- Connect Clamps Correctly: Always connect the red positive (+) clamp first, then the black negative (-) clamp to a grounded metal part of the car (away from the battery) to minimize sparks.
- Monitor and Disconnect Safely: Allow sufficient charging time, monitor the process, and disconnect the charger in reverse order (negative first).
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Clean terminals, check fluid levels (if applicable), and use a maintainer for stored vehicles to prolong battery life.
- Recognize When to Replace: Be aware of signs like persistent slow cranking or frequent charging needs, indicating your battery is at the end of its lifespan.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
Can I charge my car battery in the car?
Yes, absolutely! It’s generally safe and convenient to charge your car battery while it remains installed in the vehicle. This guide provides detailed steps on how to do it properly.
How long does it take to charge a dead car battery in the car?
The charging time depends on the battery’s discharge level, its size, and the amperage of your charger. A deeply discharged battery with a 10-amp smart charger might take 4-8 hours, while a lower-amp maintainer could take 12-24 hours or more.
Do I need to disconnect the battery terminals from the car to charge it?
No, usually you do not need to disconnect the battery terminals from the car to charge it. Modern smart chargers are designed to safely charge a battery while it’s still connected to the vehicle’s electrical system, provided all car accessories are turned off.
Is it safe to charge a car battery overnight in the car?
Yes, it can be safe if you use a modern “smart” charger or battery maintainer. These chargers automatically monitor the battery’s state and switch to a float mode or shut off when fully charged, preventing overcharging. Older, non-smart chargers should be monitored more closely.
What should I do if my car battery won’t hold a charge after charging?
If your battery won’t hold a charge, it likely needs replacement or there’s an underlying issue. This could be a failing alternator (which recharges the battery while driving), a parasitic electrical drain, or a severely damaged internal battery cell. Professional diagnosis is recommended.
📑 Table of Contents
Understanding Your Car Battery and Why It Dies
A dead car battery is frustrating, so understanding its basics helps. Your battery powers the starter motor and vehicle electronics when the engine is off. Most cars use either traditional Lead-Acid (flooded) or advanced AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) batteries. AGM batteries are sealed and maintenance-free, offering better performance and longer life. This understanding is crucial whether you need to know how to charge car battery in car or simply perform routine maintenance.
Common Causes of a Dead Battery
- Left Lights On: The classic culprit! Forgetting to turn off headlights, interior lights, or even leaving a door ajar can quickly deplete your battery’s charge.
- Infrequent Driving or Short Trips: Your alternator recharges your battery while you drive. If you only take short trips, the alternator might not have enough time to fully replenish the energy used during startup. Infrequent driving also allows the battery to self-discharge over time.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both intense cold and heat significantly reduce battery efficiency and lifespan, making it harder for the battery to deliver power or hold a charge.
- Parasitic Drain: Even when your car is off, certain components (like the clock or alarm) draw a small amount of power. An excessive “parasitic drain” from a faulty component can silently kill your battery over time.
- Old Age or Faulty Alternator: Car batteries typically last 3-5 years. Over time, their ability to hold a charge diminishes. A failing alternator means your battery isn’t getting recharged properly while you drive.
Signs of a Weak Battery
Sometimes your battery gives you warning signs before it completely quits. Look out for a slow engine crank (the engine turns over sluggishly), dim headlights or interior lights (especially when trying to start), or the “check battery” light illuminated on your dashboard. Physical signs like corrosion around the battery terminals or a swollen/cracked battery case also indicate issues.
Essential Tools for Charging Your Car Battery
To safely and effectively charge your car battery in car, you’ll need a few key pieces of equipment. Having these on hand will make the process smooth and hassle-free.
Visual guide about How to Charge Car Battery in Car
Image source: images.saymedia-content.com
Battery Charger Types
Choose a charger suitable for your needs: Smart (Automatic) Chargers are highly recommended. These intelligent chargers can detect the battery’s charge level and type, then adjust the voltage and current accordingly, preventing overcharging. They’re often the best choice when you need to know how to charge car battery in car effectively. Battery Maintainers are ideal for long-term storage, providing a low, steady charge to keep the battery topped off. Trickle Chargers are simpler, deliver a low current, and are very slow for a deeply discharged battery, requiring more monitoring. Knowing these types helps you pick the best approach when you need to figure out how to charge car battery in car.
Safety Gear and Other Helpful Items
- Safety Glasses or Goggles & Rubber Gloves: Essential for protecting your eyes from acid splashes or sparks and your hands from corrosive battery acid.
- Wire Brush and Baking Soda: For cleaning corrosive buildup (white or blue-green powder) on battery terminals. Baking soda mixed with a little water neutralizes battery acid.
- Old Rags or Towels: To wipe away corrosion and keep your work area clean.
- Owner’s Manual: Always a good idea to consult your car’s specific instructions for battery care and charging recommendations.
Gathering these tools beforehand will ensure you’re well-prepared when it’s time to learn how to charge car battery in car.
Safety First: Precautions Before You Start
Working with car batteries can be dangerous if proper precautions aren’t taken. Battery acid is corrosive, and batteries can produce explosive hydrogen gas. Always prioritize safety over speed when you charge car battery in car. These careful steps are fundamental to safely executing how to charge car battery in car without incident.
Environment and Vehicle Status
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area: Batteries release hydrogen gas during charging, which is highly flammable and explosive. Ensure you are in an open space, like a garage with the door open, or outdoors.
- No Open Flames or Sparks: Absolutely no smoking, open flames, or anything that can create a spark near the battery while charging. This includes electrical tools that might spark.
- Turn Off the Engine and All Accessories: Make sure your car’s engine is completely off. Turn off headlights, interior lights, radio, and anything else that draws power.
- Engage the Parking Brake: This prevents the car from accidentally rolling.
Personal Protection and Battery Inspection
- Wear Protective Gear: Always put on your safety glasses/goggles and rubber gloves before you begin.
- Remove Metal Jewelry: Rings, watches, and bracelets can conduct electricity, potentially causing a short circuit, severe burns, or damaging the battery if they come into contact with the terminals.
- Inspect the Battery: Before connecting anything, visually inspect the battery. Look for cracks, leaks, or swelling. If the battery casing is damaged, leaking, or severely swollen, do NOT attempt to charge it. A damaged battery could be extremely dangerous and needs professional assessment and likely replacement.
- Clean Terminals: If there’s any white or blue-green corrosion on the terminals, clean it off first. A wire brush and a paste of baking soda and water work wonders to neutralize the acid. Rinse with plain water and dry thoroughly before connecting the charger. Corrosion can impede proper charging.
- Check Fluid Levels (for Flooded Batteries): If you have a traditional flooded lead-acid battery with removable caps, gently pry them off and check the electrolyte levels. If they are low, add distilled water (NOT tap water) to just cover the plates. Do this before charging. Do not overfill. AGM and EFB batteries are sealed and do not require this.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Charge Car Battery in Car
Now that you’re prepared with the right tools and safety precautions, let’s get down to the actual process of how to charge car battery in car. Follow these steps carefully for a safe and effective charge.
Step 1: Preparing Your Battery
- Confirm Safety: Double-check that your vehicle is off, parking brake engaged, and all accessories are off. Put on your safety glasses and gloves.
- Clean Terminals: If not already done during your safety checks, use a wire brush and a baking soda-water paste to remove any corrosion from the battery terminals. Rinse with water and dry completely. This ensures a good electrical connection.
- Check Fluid (if applicable): For traditional flooded batteries with removable caps, gently remove them and check the electrolyte levels. If low, top up with distilled water to just cover the plates. Replace caps loosely to allow gases to escape during charging. Skip this for sealed batteries.
Step 2: Connecting the Charger
This is where precision matters. The connection sequence is crucial to prevent sparks near potentially flammable hydrogen gas.
- Connect the Red (Positive) Clamp First: Attach the red positive (+) clamp from the charger to the positive (+) terminal on your car battery. The positive terminal is usually larger and marked with a plus sign, often covered with a red cap.
- Connect the Black (Negative) Clamp Second (Crucial Step):
- Recommended Method: Connect the black negative (-) clamp from the charger to an unpainted, sturdy metal part of the car’s frame or engine block, away from the battery. This provides a safe ground connection and minimizes the risk of sparks occurring directly near the battery, where hydrogen gas might be present.
- Alternative (if specifically instructed by charger/manual): In some cases, or with specific battery maintainers, you might connect the black negative (-) clamp directly to the negative (-) terminal on the car battery. Only do this if your vehicle owner’s manual or charger instructions explicitly advise it. If you observe sparks when connecting, immediately disconnect and use the recommended grounding method.
- Ensure Secure Connections: Wiggle both clamps gently to ensure they have a solid, firm connection to the terminals or ground point. Loose connections can lead to inefficient charging or dangerous arcing.
Step 3: Setting the Charger and Initiating Charge
Once connected, it’s time to turn on the charger.
- Plug In the Charger: ONLY plug the battery charger into the wall outlet after all clamps are securely connected to the battery and/or vehicle ground.
- Select Settings (if applicable): If your charger has settings for battery type (e.g., standard, AGM, gel) or charge rate (e.g., 2A, 10A, 20A), select the appropriate ones. For most car batteries, a 10-amp setting is a good balance between speed and battery health. Lower amperage (2-5 amps) is slower but gentler, ideal for a maintenance charge. Always refer to your charger’s manual.
- Start Charging: Turn on the charger. Most smart chargers will display the charging status, current voltage, or estimated time.
Step 4: The Charging Process
Patience is key here. Charging a deeply discharged car battery can take time. Understanding the expected duration is vital for correctly knowing how to charge car battery in car.
- Duration: How long it takes to charge car battery in car depends on its size, how discharged it is, and the amperage of your charger. A deeply discharged standard car battery might take anywhere from 4-8 hours with a 10-amp charger, or significantly longer (12-24+ hours) with a lower-amp maintainer. For a completely dead battery, it could even take a full day. Consult your charger’s manual for expected charging times.
- Monitoring: Periodically check on the charging process. Ensure the charger isn’t overheating and that there are no unusual smells or sounds coming from the battery. Some smart chargers have indicator lights that show when charging is complete or if there’s an error.
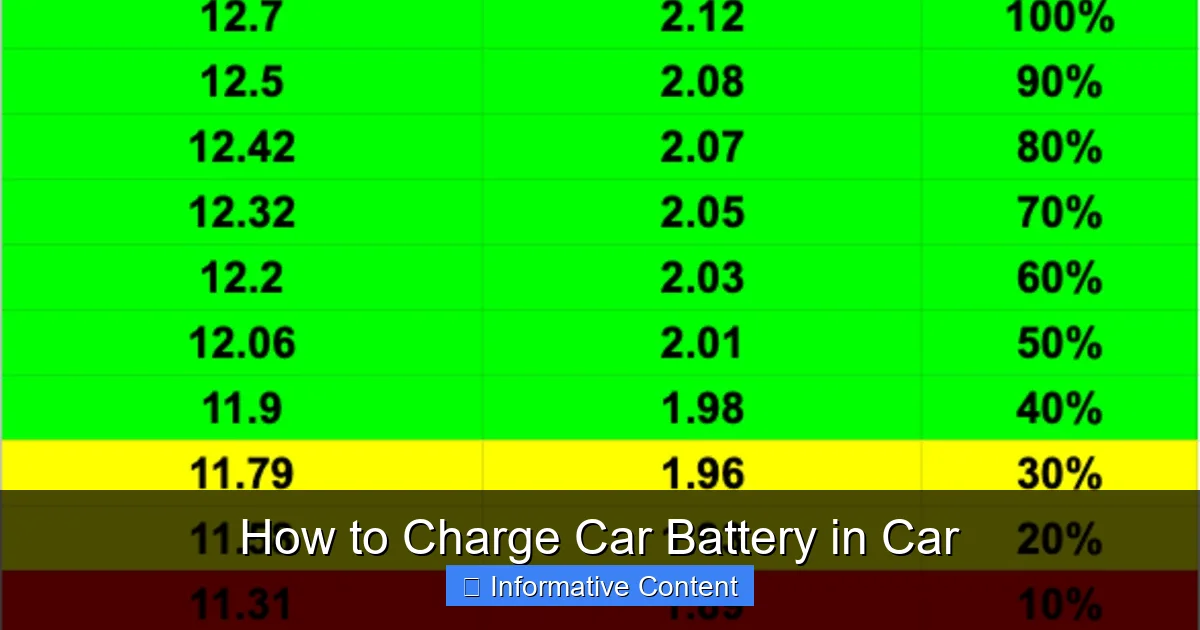
- Avoid Overcharging: Modern smart chargers will automatically switch to a “float” mode or shut off when the battery is fully charged, preventing overcharging which can damage the battery. If you’re using an older, non-smart charger, you’ll need to monitor it more closely and disconnect it once the battery reaches full voltage (typically around 12.6-12.8 volts for a 12V battery).
Step 5: Disconnecting the Charger
Just like connecting, disconnection has a specific, safe order to prevent sparks.
- Turn Off the Charger: First, switch off the battery charger.
- Unplug from Wall: Then, unplug the charger from the electrical wall outlet.
- Remove Black (Negative) Clamp: Carefully remove the black negative (-) clamp from the car’s frame/engine block or the negative terminal.
- Remove Red (Positive) Clamp: Finally, remove the red positive (+) clamp from the battery’s positive terminal.
- Replace Battery Caps/Cover: If you removed any battery caps, replace them securely. If there’s a battery cover, put it back in place.
You’re all done! Attempt to start your car. If it starts, great! If not, there might be a deeper issue at play, requiring further troubleshooting.
Beyond Charging: Maintenance Tips and Troubleshooting
Knowing how to charge car battery in car is a fantastic skill, but prevention is always better than cure. Regular maintenance can extend your battery’s life and help you avoid future dead battery surprises. Beyond the immediate task of learning how to charge car battery in car, proactive maintenance is key for battery longevity. If charging doesn’t work, other issues might be present.
Regular Battery Maintenance
- Keep Terminals Clean: Periodically check your battery terminals for corrosion. Clean them with a wire brush and baking soda solution whenever necessary. Clean terminals ensure good electrical flow.
- Check Cables: Ensure battery cables are securely attached and not frayed or damaged.
- Monitor Fluid Levels (Flooded Batteries): If you have a traditional flooded lead-acid battery, check the electrolyte levels regularly (e.g., every 3-6 months) and top up with distilled water if needed.
- Use a Battery Maintainer for Stored Vehicles: If you store your car for extended periods or don’t drive it frequently, connect it to a battery maintainer. This keeps the battery topped off without overcharging, preventing self-discharge and extending its life.
- Drive Regularly: Take your car for a decent drive (at least 20-30 minutes) regularly to allow the alternator to fully charge the battery.
When to Replace Your Battery
Even with the best care, car batteries don’t last forever. Most have a lifespan of 3-5 years. If you often find yourself needing to figure out how to charge car battery in car, it’s a sign your battery is failing. Watch for these other signs that it might be time for a replacement:
- Persistent Slow Cranking: Even after charging, if your engine consistently cranks slowly, it’s a strong indicator.
- Frequent Need for Charging: If you find yourself needing to charge your car battery in car very often, the battery might not be holding a charge well anymore.
- Battery Light Stays On: If the battery light on your dashboard stays on even after driving for a while, it could mean the battery isn’t taking a charge, or there’s an alternator issue.
- Age: If your battery is past its typical lifespan, it’s generally good practice to have it tested, especially before winter.
- Swollen Battery Case: A physical sign of internal damage, often caused by overcharging or extreme heat. This battery is dangerous and needs immediate replacement.
Many auto parts stores offer free battery testing. It’s a quick way to assess its health.
What if Charging Doesn’t Work?
If you’ve followed all the steps to charge car battery in car, and your car still won’t start, or the battery dies again quickly, the problem might not be just the battery itself. Here are other potential culprits:
- Faulty Alternator: The alternator is responsible for charging the battery while the engine runs. If it’s not working, your battery won’t get recharged. You might notice dimming lights while driving or a burning smell.
- Bad Starter Motor: The starter motor is what physically turns the engine over. If it’s faulty, you might hear a single click or nothing at all when you try to start, even with a fully charged battery.
- Excessive Parasitic Drain: An electrical component staying on when the car is off can slowly kill the battery. This can be tricky to diagnose and often requires a professional.
- Severely Damaged Battery: If the battery is old or has internal damage (e.g., a shorted cell), it may simply be incapable of holding a charge, no matter how much you try to charge it.
In these cases, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic to diagnose and fix the underlying issue.
Conclusion
A dead car battery is inconvenient, but knowing how to charge car battery in car is a valuable skill. By following this guide, you can safely and effectively revive your vehicle’s power source without professional help. Remember to prioritize safety with protective gear and proper ventilation, and always follow the correct connection and disconnection sequence. Regular maintenance and a proactive approach to battery health will significantly extend its life, providing you with reliable starts and peace of mind on every journey. Stay empowered and stay charged!
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of battery charger should I use?
For most users, a “smart” or automatic battery charger is recommended. These intelligent chargers adjust the charging rate based on your battery’s condition, preventing overcharging and optimizing battery health. Battery maintainers are also excellent for long-term storage, especially for infrequently used vehicles.
Can I charge an AGM battery with a regular charger?
It’s best to use a smart charger with an AGM setting. While some regular chargers might work, AGM batteries require specific voltage regulation to prevent damage and maximize lifespan. Using an inappropriate charger can shorten an AGM battery’s life or damage it.
What does a “parasitic drain” mean?
A parasitic drain refers to a continuous draw of power from your car battery even when the vehicle is turned off. This can be caused by faulty electrical components like interior lights, radio memory, or an alarm system that doesn’t fully shut down, slowly killing your battery over time.
Is corrosion on battery terminals bad?
Yes, corrosion on battery terminals is detrimental. It indicates a chemical reaction that impedes proper electrical flow, making it harder for your battery to charge and for your starter to draw power. Always clean corrosion using a wire brush and a baking soda solution to ensure good conductivity.
How often should I check my car battery?
It’s a good practice to visually inspect your battery and its terminals every few months, especially before winter or hot summer months. If you have a flooded lead-acid battery with removable caps, check the fluid levels at the same frequency. Consider getting your battery professionally tested annually.
What if my battery is swollen or leaking?
If your battery is swollen, cracked, or leaking, do not attempt to charge it. This indicates severe internal damage and poses a significant explosion and chemical burn risk. Such a battery is dangerous and needs to be replaced immediately by a professional or at an authorized service center.