Keeping your car battery charged is essential for reliable vehicle operation, and it’s largely thanks to a clever system working behind the scenes. This article will explain how your car’s charging system, led by the alternator and voltage regulator, continuously replenishes your battery, powers electrical components, and ensures your vehicle starts every time. We’ll break down the process, common issues, and practical tips to keep everything running smoothly.
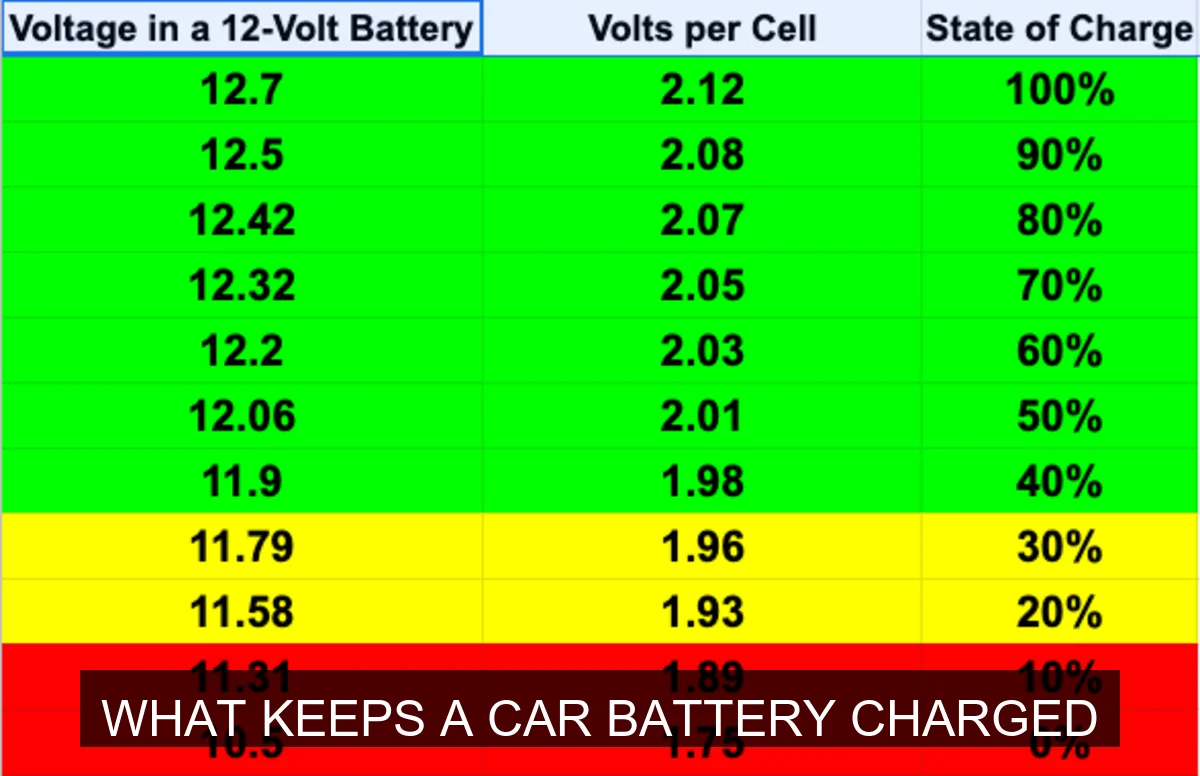
Image source: Saymedia-content
📋 Table of Contents
- 🔹 Introduction: The Unsung Heroes of Your Car’s Power
- 🔹 What Keeps a Car Battery Charged? The Core System Explained
- 🔹 Why is a Properly Charged Car Battery So Important?
- 🔹 How Does the Car’s Charging System Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- 🔹 Key Components of the Charging System
- 🔹 Beyond the Alternator: Other Factors Affecting Battery Charge
- 🔹 Common Myths and Misconceptions About Car Battery Charging
- 🔹 Practical Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s Charging System
- 🔹 Real-Life Scenarios: When Your Battery Might Struggle
- 🔹 People Also Ask (FAQ)
- 🔹 Conclusion: Keeping Your Car Powered Up
What keeps a car battery charged is primarily the alternator, a crucial component that generates electricity while your engine runs. This electricity powers the vehicle’s systems and simultaneously recharges the 12-volt battery, ensuring it has enough juice to start the car again and support accessories when the engine is off.
Introduction: The Unsung Heroes of Your Car’s Power
Have you ever wondered why your car battery doesn’t just run out of power after a few starts? It’s a great question, and the answer lies in a remarkably clever system designed to keep things running smoothly. Your car battery isn’t just a static power source; it’s part of a dynamic electrical network that constantly generates and replenishes its charge. Understanding this system is key to appreciating how your vehicle works and keeping it reliable.
In this article, we’re going to dive deep into the fascinating world of automotive charging. We’ll explore the main components that tirelessly work to keep your battery charged, explain how they interact, and offer practical insights into maintaining this vital system. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of what keeps a car battery charged and why it’s so important for every driver.
What Keeps a Car Battery Charged? The Core System Explained
At its heart, what keeps a car battery charged is an intricate dance between three main players: the alternator, the voltage regulator, and the car battery itself. Think of your car battery as a storage tank for electrical energy. When you start your car, it uses a lot of that stored energy. Without a way to refill that tank, you’d quickly be stranded.
That’s where the charging system steps in. Once the engine is running, it spins the alternator, which acts like a mini power plant. The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. This electricity is then managed by the voltage regulator, which ensures the battery receives the correct amount of charge – not too much, not too little. This constant replenishment is what prevents your battery from dying and keeps all your car’s electrical systems humming.
Why is a Properly Charged Car Battery So Important?
A fully charged car battery isn’t just about starting your car. It’s the backbone of your vehicle’s entire electrical system. Here’s why keeping it in tip-top shape truly matters:
- Reliable Starts: This is the most obvious benefit. A strong battery provides the surge of power needed to crank the engine. Without it, your car simply won’t start.
- Powering Accessories: When your engine isn’t running, your battery powers everything from your radio and lights to your power windows and dashboard clock.
- Supporting Engine Electronics: Modern cars are packed with computers and sensors. These critical components need a stable, consistent power supply, which the battery helps provide.
- Extending Battery Lifespan: Allowing a battery to repeatedly drain completely can significantly shorten its overall life. Keeping it properly charged helps maintain its health and capacity.
- Safety Features: Essential safety systems like airbags, anti-lock brakes (ABS), and electronic stability control (ESC) rely on a robust electrical system.
In essence, a happy, charged battery means a happy, reliable car. Ignoring its health can lead to unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs.
How Does the Car’s Charging System Work? A Step-by-Step Breakdown
It might seem like magic, but the process of keeping your car battery charged is a well-engineered cycle. Let’s break it down simply:
- Engine Starts: The car battery sends a powerful electrical current to the starter motor, which cranks the engine to life. This uses a lot of battery power.
- Alternator Activates: Once the engine is running, it spins a belt connected to the alternator. The alternator then begins generating electricity.
- Current Conversion: Inside the alternator, this electricity (AC) is converted into direct current (DC) – the type your battery and car systems use.
- Voltage Regulation: A crucial component, the voltage regulator, ensures this DC power is at the correct voltage (around 13.5 to 14.5 volts). This prevents overcharging or undercharging the battery.
- Recharging & Powering: The regulated electricity flows to the battery, recharging it after the start. At the same time, this power runs all the car’s electrical components like lights, radio, and engine computer.
- Continuous Cycle: As long as the engine runs, this process continues, keeping your battery topped up and your electrical systems powered.
This continuous cycle is the core mechanism that keeps a car battery charged throughout your drive.
Key Components of the Charging System
To really understand what keeps a car battery charged, we need to know the main parts involved:
| Component | Primary Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Alternator | Generates electricity from engine’s mechanical energy. Powers car and recharges battery. | The car’s power plant. |
| Voltage Regulator | Controls alternator’s output voltage. Prevents over or undercharging. | The electrical traffic cop. |
| Car Battery | Stores electrical energy to start engine and power accessories when off. | The energy storage tank. |
| Wiring & Cables | Connects all components, providing pathways for electrical current. | The car’s electrical highway. |
| Serpentine Belt | Transfers mechanical power from engine to alternator and other parts. | The power transmission belt. |
All these parts must work together for the charging system to keep a car battery charged effectively.
Beyond the Alternator: Other Factors Affecting Battery Charge
While the alternator is vital, other things can influence your battery’s charge level:
- Parasitic Drains: Small electrical components (like the clock or alarm) that draw power even when the car is off. Too much draw can slowly kill your battery.
- Driving Habits: Frequent short trips don’t give the alternator enough time to fully recharge the battery after starting.
- Extreme Temperatures: Both very hot and very cold weather can reduce battery efficiency and lifespan.
- Battery Age and Health: Batteries wear out, usually lasting 3-5 years. An old battery can’t hold a charge as well, no matter how good the charging system.
- Corrosion or Loose Connections: Dirty or loose battery terminals can prevent proper current flow, hindering charging.
These factors help explain why a battery might still run low even with a working alternator.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Car Battery Charging
Let’s clarify some common misunderstandings about car batteries and their charging:
Myth 1: Idling your car will fully charge the battery quickly.
Reality: Idling charges the battery very slowly, and often not enough to replace the power used to start the car, especially in modern vehicles with high electrical demands. Driving at normal speeds for 20-30 minutes is far more effective.
Myth 2: If the battery dies, it’s always the battery’s fault.
Reality: A dead battery is often a symptom, not the cause. It could point to a failing alternator, a bad voltage regulator, or a significant parasitic electrical drain in the car’s system.
Knowing the facts helps in proper car maintenance.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s Charging System
You can easily help keep your car battery charged and its system healthy:
- Drive Regularly: Take your car for at least a 20-30 minute drive at highway speeds once a week if you usually only do short trips.
- Limit Off-Engine Accessories: Avoid using the radio, lights, or charging devices for long periods when your engine isn’t running.
- Keep Terminals Clean: Inspect battery terminals for corrosion. Clean them with a wire brush if you see fuzzy, white, or greenish buildup.
- Test Your Battery: Have your battery’s health checked periodically, especially if it’s over three years old. Many auto parts stores offer free testing.
- Turn Off Lights: Always double-check that all lights (headlights, interior, trunk) are off when you leave your car.
- Consider a Battery Maintainer: If you store your car for extended periods, a battery maintainer (or trickle charger) can keep it at an optimal charge.
These simple actions can extend your battery’s life and ensure your charging system works efficiently.
Real-Life Scenarios: When Your Battery Might Struggle
Here are a couple of situations where the charging system might face challenges:
Scenario 1: The Short Commuter’s Dilemma
Someone drives their car only five minutes to work and five minutes back each day. Each start uses a fair amount of battery power. The short drive time isn’t enough for the alternator to fully replenish that lost charge. Over weeks, the battery slowly discharges further and further, until one cold morning, it simply can’t crank the engine.
Scenario 2: The Dimming Headlights
You notice your headlights get noticeably dimmer when your car is idling, but brighten up when you accelerate. This often indicates the alternator isn’t producing enough power at low engine RPMs, or the voltage regulator isn’t maintaining consistent voltage. The battery tries to compensate, but it’s a sign the charging system is underperforming.
People Also Ask (FAQ)
What is the main component that keeps a car battery charged?
The main component that keeps a car battery charged is the alternator. It’s driven by the engine and generates the electricity needed to power the car and recharge the battery.
Why is maintaining a car battery charge important for vehicle longevity?
Maintaining a proper car battery charge is important for vehicle longevity because it prevents stress on the battery, starter, and other electrical components. A well-maintained charge extends battery life and ensures consistent power for all vehicle systems, reducing the risk of premature failures.
How does an alternator actually recharge the battery?
An alternator recharges the battery by converting the engine’s mechanical rotation into electrical energy. This alternating current (AC) is then rectified into direct current (DC) and regulated to a specific voltage (around 13.5-14.5 volts) before being sent to the battery, topping up its charge and powering the car’s electrical needs.
Is it normal for a car battery to lose charge when the car is off?
Yes, it is normal for a car battery to lose a very small amount of charge when the car is off. This is due to “parasitic draws” from essential systems like the clock, alarm, and computer memory. However, a rapid or significant loss of charge indicates an abnormal issue.
When should I worry about my car’s charging system?
You should worry about your car’s charging system if you see the battery warning light on your dashboard, your headlights dim significantly at idle, accessories fail intermittently, or your car becomes difficult to start consistently. These are signs the system might not be effectively keeping your car battery charged.
Conclusion: Keeping Your Car Powered Up
Understanding what keeps a car battery charged is fundamental to knowing how your vehicle operates reliably. It’s not just about the battery; it’s about the entire charging system working in harmony. The alternator, voltage regulator, and battery form a critical trio that ensures you have reliable power for starting your engine and running all your car’s electrical systems.
By grasping the mechanics behind this process and adopting good maintenance habits, you can significantly extend the life of your battery, avoid unexpected breakdowns, and ensure your car remains a dependable mode of transport. Pay attention to the subtle cues your car gives you, and you’ll be well-equipped to keep its electrical heart beating strong.