A fully charged 12V car battery should ideally measure between 12.6 and 12.8 volts when the engine is off and the battery has rested for at least an hour. This static voltage is a critical indicator of its health; readings below 12.4V suggest it needs charging, while anything below 12.0V points to a severely depleted or potentially failing battery. Always test with a multimeter for an accurate assessment of its charge level and overall condition.
Hey there, fellow driver! Have you ever walked out to your car, turned the key, and… nothing? Just that dreaded click-click-click, or worse, absolute silence? It’s a feeling we all know and absolutely dread. Our car battery, often overlooked until it fails us, is the unsung hero that kick-starts our daily adventures. But how often do we actually think about its health, beyond just hoping it works every morning?
One of the most common questions that pops into mind when battery troubles arise, or when you’re just being proactive, is about its charge level. Specifically, people often wonder, “exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have?” It’s a crucial question, because understanding this single measurement can tell you a world about your battery’s well-being, its remaining life, and whether it’s truly ready to power your vehicle through thick and thin.
Think of your car battery’s voltage like a personal health metric. Just as a doctor checks your blood pressure or temperature, checking your battery’s voltage gives you an immediate snapshot of its condition. In this comprehensive guide, we’re going to dive deep into the world of car battery voltage, demystifying what those numbers mean and, most importantly, answering the core question: exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have? We’ll make it simple, clear, and just like chatting with a friend who happens to know a lot about cars!
Key Takeaways
- Fully Charged: A 12V car battery should read 12.6V to 12.8V.
- Accurate Test: Measure voltage after the car has rested for hours.
- Low Voltage Sign: Below 12.4V indicates a partially discharged battery.
- Charging System: Engine running, voltage should be between 13.7V and 14.7V.
- Battery Health: Consistently maintain a full charge to extend battery life.
- Avoid 12.0V: A truly fully charged 12V battery is never 12.0V.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
What’s the ideal voltage for a fully charged car battery?
A fully charged car battery, when resting and healthy, should typically measure between 12.6 to 12.8 volts. This range confirms your battery is in prime condition and ready to deliver consistent power.
Why isn’t a “12-volt battery” exactly 12 volts when fully charged?
That’s a common and great question! While we call it a “12-volt battery,” that’s its nominal voltage. A truly healthy, fully charged car battery needs to produce slightly more than 12 volts to ensure it can effectively crank your engine and power your vehicle’s systems.
What if my battery reads below 12.6 volts? Is it still fully charged?
If your car battery reads below 12.6 volts, it’s not fully charged. A reading of 12.4 volts or less indicates it’s significantly discharged and likely needs a charge, while anything below 12 volts suggests a deeply discharged or potentially failing battery.
How do I check how many volts my fully charged car battery has?
You can easily check the voltage with a simple multimeter. Just connect the red probe to the positive (+) terminal and the black probe to the negative (-) terminal while your car’s engine is off.
When is the best time to check the voltage for an accurate reading?
For the most accurate measurement of how many volts your fully charged car battery has, check it after the car has been turned off for at least a few hours, ideally overnight. This allows any “surface charge” to dissipate, giving you a true resting voltage.
📑 Table of Contents
- Understanding Your Car Battery’s Core Function
- The Magic Number: Exactly How Many Volts is “Fully Charged”?
- Measuring Battery Voltage: Your Essential Tools and Techniques
- What Different Voltage Readings Tell You (and What to Do About It)
- Factors Affecting Car Battery Voltage and Lifespan
- Maintaining Optimal Battery Health: Practical Tips
- Car Battery Voltage: State of Charge Guide
- Conclusion
Understanding Your Car Battery’s Core Function
More Than Just a Power Source
Before we pinpoint exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have, let’s take a moment to appreciate what this humble box of chemicals and metal actually does. Your car battery isn’t just there to start your engine; it’s a vital component that provides power to all the electrical components of your vehicle when the engine isn’t running. Think about your radio, your lights, the power windows, even the memory for your infotainment system – they all rely on the battery for power before the alternator takes over once the engine is running.
It acts like a buffer, smoothing out the electrical supply from the alternator and providing a stable voltage for your car’s sensitive electronics. Without a healthy battery, even if your alternator is perfectly fine, your car would struggle to start, and its electrical system would suffer from inconsistent power delivery.
The Chemical Magic Inside
Most car batteries today are 12-volt lead-acid batteries. This means they are comprised of six individual cells, each producing approximately 2.1 to 2.2 volts when fully charged. These six cells are connected in series, adding up their individual voltages to give you the total battery voltage. The “lead-acid” part refers to the internal chemistry: lead plates (positive and negative) immersed in an electrolyte solution of sulfuric acid and water.
When you start your car or use electrical accessories, a chemical reaction occurs, generating electricity. When the alternator charges the battery, this chemical reaction reverses, storing energy for later use. It’s a continuous cycle, and knowing exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have helps us understand if this cycle is working as it should.
The Magic Number: Exactly How Many Volts is “Fully Charged”?
The Ideal Resting Voltage
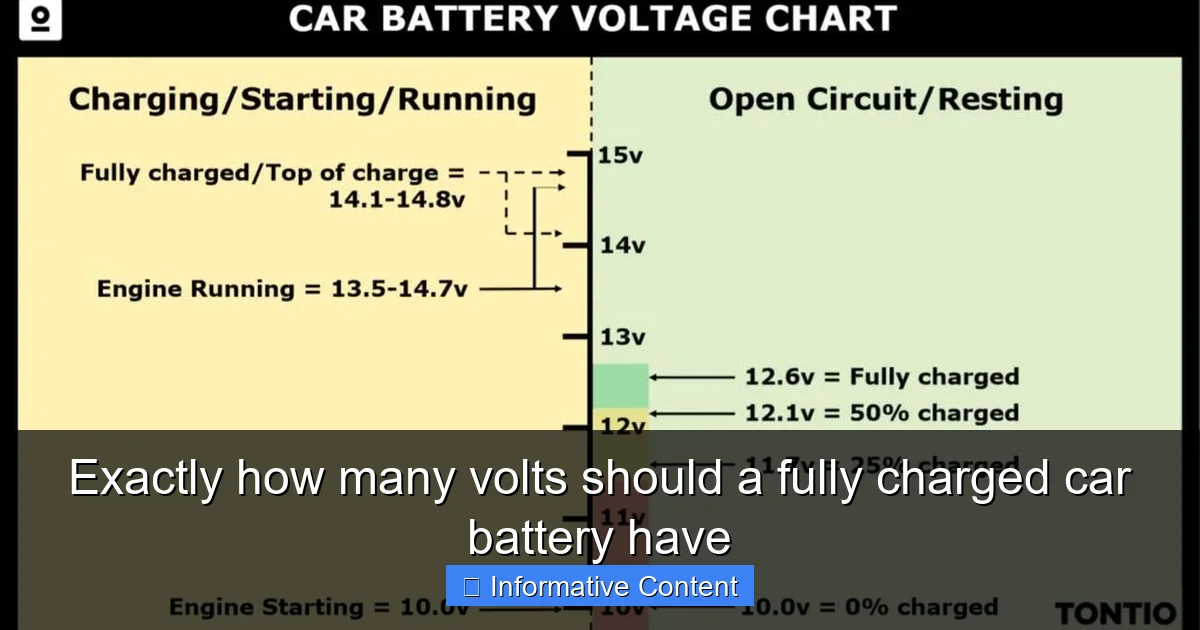
Okay, let’s get right to the heart of the matter. If you’re checking your car battery when the engine is off (this is called its “resting voltage”), exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have? The answer for a healthy, fully charged 12-volt lead-acid car battery should be between 12.6 and 12.8 volts. This is the golden range you’re aiming for. Anything consistently below 12.4 volts without any load usually indicates a state of partial discharge or a potential issue.
Visual guide about fully charged car battery voltage
Image source: tontio.com
It’s important to check this “resting voltage” after your car has been sitting for a few hours, ideally overnight, and definitely not right after you’ve turned the engine off. This allows any “surface charge” from the alternator to dissipate, giving you a true reading of the battery’s internal charge.
Why 12.6 Volts (and a Bit More) Matters
That 12.6-12.8 volt range represents the battery at its peak, ready to deliver optimal cranking power and sustain your car’s electrical needs. When a car battery is at 12.6 volts, it’s considered to be at 100% state of charge. Even a slight drop can indicate a significant reduction in available power. For instance, a battery reading 12.4 volts is only about 75% charged, and 12.0 volts is roughly 25% charged. You can see how quickly the percentage drops with just a small change in voltage.
Understanding exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have isn’t just about knowing a number; it’s about understanding what that number signifies for your car’s reliability. A battery that consistently fails to reach this threshold, even after charging, is signaling that its end might be near.
Measuring Battery Voltage: Your Essential Tools and Techniques
The Digital Multimeter: Your Best Friend
To accurately answer exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have for your specific vehicle, you’ll need a simple tool: a digital multimeter. These are readily available at any auto parts store or hardware store, and they’re relatively inexpensive. It’s an indispensable tool for any DIY car enthusiast or simply someone who wants to keep an eye on their vehicle’s health.

Visual guide about fully charged car battery voltage
Image source: cdn.shopify.com
A multimeter can measure voltage, current, and resistance. For battery testing, you’ll set it to measure DC (direct current) voltage, usually indicated by “V—” or “VDC” on the dial, and select a range suitable for 12-volt systems, typically 20V.
Step-by-Step Voltage Testing
Here’s how you can check how many volts should a fully charged car battery have:
- Gather Your Tools: You’ll need your digital multimeter and possibly some safety gloves and glasses.
- Ensure the Car is Off: Make sure the engine is completely off and has been for at least a few hours (preferably overnight) to get an accurate resting voltage reading. All accessories should be off.
- Pop the Hood: Locate your car battery.
- Set Your Multimeter: Turn the dial to DC voltage (VDC) and set it to the 20-volt range.
- Connect the Probes:
- Connect the red (positive) probe to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Connect the black (negative) probe to the negative (-) terminal of the battery.
- Read the Display: The number on the multimeter’s screen is your battery’s resting voltage. Compare this to the ideal range for how many volts should a fully charged car battery have (12.6-12.8V).
If you’re testing while the engine is running, you’ll be checking your alternator’s output, not just the battery’s resting charge. While running, the voltage should be higher, typically between 13.7 and 14.7 volts, indicating that the alternator is charging the battery effectively.
Load Testing vs. Resting Voltage
While knowing exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have via a resting voltage test is helpful, it doesn’t tell the whole story. A resting voltage test indicates the battery’s surface charge, but not necessarily its ability to deliver high current under load. For that, a load test is required. A load tester applies a controlled electrical load to the battery and measures its voltage drop. If the voltage drops significantly under load, even if the resting voltage was good, it indicates a weak battery. Most auto parts stores can perform a free load test for you, which is a great way to confirm your battery’s true health.
What Different Voltage Readings Tell You (and What to Do About It)
Once you’ve tested and seen how many volts your car battery actually has, it’s time to interpret those numbers. Knowing what exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have is just the first step; understanding the deviations is where the real insight comes in.
Below 12.4 Volts: Signs of Trouble
- 12.4 Volts: Your battery is around 75% charged. It’s not critical yet, but it’s a good idea to consider giving it a charge, especially if it’s consistently at this level or lower after a drive.
- 12.0 Volts: This indicates only about a 25% charge. At this point, you’re likely to experience slow cranking or difficulty starting your car, especially in cold weather. It’s definitely time for a full charge, and you should investigate why it got this low.
- Below 12.0 Volts: Your battery is significantly discharged, potentially to the point of being unable to start your car. Leaving a battery in this state for an extended period can lead to sulfation, a process where lead sulfate crystals build up on the plates, permanently reducing the battery’s capacity and lifespan. At this point, you might need a jump start and a long, slow charge. If it repeatedly drops to this level, it’s likely time for a replacement.
The Charging System’s Role: Alternator Output
While understanding exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have is crucial, it’s equally important to know if your car’s charging system is doing its job. With the engine running, your alternator should be charging the battery. As mentioned earlier, the voltage across the battery terminals should be higher, typically between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. If it’s significantly lower (e.g., below 13.0 volts), your alternator might be failing, or there could be an issue with the charging system wiring. If it’s consistently above 15 volts, that could indicate overcharging, which is also detrimental to battery life.
Overcharging: A Less Common But Serious Threat
While undercharging and a weak battery are more common concerns, overcharging is also a danger. If your alternator consistently pushes too high a voltage (above 15 volts), it can cook the electrolyte within the battery, causing it to boil off. This reduces the electrolyte level, exposes the lead plates, and can lead to permanent damage and premature battery failure. This often manifests as a rotten egg smell (sulfur dioxide gas) coming from the battery.
Factors Affecting Car Battery Voltage and Lifespan
Knowing exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have is a great benchmark, but several external and internal factors can influence its ability to reach and maintain that optimal voltage.
Temperature’s Impact
Temperature is perhaps the biggest environmental factor affecting battery performance. In cold weather, the chemical reactions inside the battery slow down, reducing its ability to deliver current. This is why many batteries fail on the first really cold morning of winter. Conversely, extreme heat can accelerate internal corrosion and evaporation of the electrolyte, also shortening battery life. The ideal operating temperature for a car battery is around 77°F (25°C).
Age and Usage Habits
Like anything else, car batteries don’t last forever. Most lead-acid batteries have a lifespan of 3-5 years. As they age, their internal components degrade, and their ability to hold a full charge and deliver high cranking amps diminishes. Short trips, where the alternator doesn’t have enough time to fully recharge the battery after starting, also contribute to premature aging. Frequent deep discharges (letting the battery drain completely) are also very damaging.
Parasitic Drains
A “parasitic drain” refers to any electrical component in your car that draws power even when the ignition is off. Things like interior lights left on, a faulty radio, or even a sticking relay can slowly but surely drain your battery over time, preventing it from staying at exactly how many volts a fully charged car battery should have. If your battery keeps losing charge even when the car is off, it might be worth investigating for such a drain.
Maintaining Optimal Battery Health: Practical Tips
Now that you know exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have, let’s talk about how to keep yours in tip-top shape and prolong its life.
Regular Check-ups
Periodically checking your battery’s resting voltage with a multimeter is one of the easiest and most effective ways to monitor its health. Aim to do this every few months, or more frequently if your battery is older or you live in an extreme climate. Remember, 12.6-12.8 volts is what exactly how many volts a fully charged car battery should have when resting.
Proper Charging Practices
- Use a Battery Maintainer: If you don’t drive your car often, or if you store it for extended periods, a battery maintainer (or “trickle charger”) is your best friend. It keeps the battery topped off at its ideal voltage without overcharging, ensuring it always has exactly how many volts a fully charged car battery should have.
- Full Recharges: If your battery gets discharged, make sure to fully recharge it as soon as possible. Avoid leaving it in a discharged state.
- Avoid Deep Discharges: Try not to let your battery drain completely. Each deep discharge takes a toll on its lifespan.
Keeping it Clean
Corrosion build-up on the battery terminals can impede the flow of electricity, making it harder for the battery to deliver power and receive a charge. Periodically inspect your battery terminals for white or greenish powdery residue. If you see any, disconnect the battery (negative first, then positive) and clean the terminals with a wire brush and a mixture of baking soda and water. Reconnect (positive first, then negative) and apply some dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
Car Battery Voltage: State of Charge Guide
This table offers a quick reference for understanding what your battery’s resting voltage reading (after being off for several hours) likely means:
| Resting Voltage (DC) | Approximate State of Charge | Indication / Action |
|---|---|---|
| 12.6V – 12.8V | 100% | Fully charged, optimal health. This is exactly how many volts a fully charged car battery should have. |
| 12.4V | 75% | Partially discharged. Consider charging soon. |
| 12.2V | 50% | Half charged. Recharge immediately to prevent damage. |
| 12.0V | 25% | Low charge. Likely to cause starting problems. Full recharge required. |
| Below 12.0V | 0-25% | Severely discharged. Risk of sulfation and permanent damage. May not start car. |
| 13.7V – 14.7V (Engine Running) | N/A | Alternator charging properly. |
Conclusion
So, there you have it! The definitive answer to “exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have” is between 12.6 and 12.8 volts when your car has been resting for a few hours. This simple number holds the key to understanding your battery’s health and anticipating potential issues before they leave you stranded. By regularly checking this voltage, you’re not just performing a task; you’re taking a proactive step in maintaining your car’s reliability and extending the life of one of its most critical components.
Remember, your car battery is the heart of your vehicle’s electrical system. Giving it a little attention, understanding its language (voltage readings!), and knowing what exactly how many volts should a fully charged car battery have will empower you to keep your car running smoothly. So grab that multimeter, become your own car battery detective, and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with a healthy, fully charged power source under the hood!
Stay safe on the road, and happy driving!
🎥 Related Video: What Voltage Should Car Battery Be?!
📺 Mechanic Mindset
Using the voltmeter to quickly assess the battery state of charge. What voltage should a car battery read?! Link to BUY Ancel …
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the ideal voltage for a fully charged car battery?
A healthy, fully charged car battery should typically measure around 12.6 to 12.8 volts when the engine is off and it has rested for a few hours. This reading indicates that all six cells in the 12-volt battery are functioning optimally and it’s at its peak capacity.
Is 12.4 volts considered fully charged for a car battery?
No, 12.4 volts indicates that your car battery is only about 75% charged, not fully charged. While it might still start your car, it suggests the battery is not at its peak capacity and may need a recharge to prevent premature wear.
How do I accurately measure the volts of my car battery?
To accurately measure the volts of your car battery, use a digital multimeter set to DC volts. Connect the red probe to the positive (+) terminal and the black probe to the negative (-) terminal, ensuring the engine is off and the battery has rested for at least an hour for the most accurate reading.
What should I do if my fully charged car battery shows low volts?
If your supposedly fully charged car battery consistently shows low volts (below 12.4V), it might indicate a problem with the charging system or the battery itself. You should consider having it professionally tested to determine if it needs recharging, has a failing cell, or if your alternator isn’t working correctly.
Why might my fully charged car battery read 12.8 volts sometimes and 12.6 volts other times?
Slight variations in volts for a fully charged car battery can occur due to factors like ambient temperature, the specific type of battery (e.g., AGM vs. standard flooded), and how long it has rested after charging. Both 12.6V and 12.8V generally fall within the healthy range for a well-maintained battery.
What volts should a car battery have when the engine is running?
When your car’s engine is running, the charging system (alternator) should be supplying power, and your car battery’s reading should be higher, typically between 13.7 and 14.7 volts. This higher voltage indicates that the alternator is properly charging the battery and powering the vehicle’s electrical system.