To safely and effectively charge your AGM car battery, always prioritize using a smart charger with a dedicated AGM mode, as improper charging can severely damage these sensitive batteries. Ensure correct positive-to-positive and negative-to-negative connections in a well-ventilated area, then simply monitor until fully charged to prevent overcharging and maximize battery lifespan.
Ever found yourself staring at a dead car battery, feeling that familiar pang of frustration? We’ve all been there. It’s a rite of passage for many vehicle owners. But what if your car relies on an AGM battery, and you’ve heard these aren’t quite like the traditional ones? You’d be right to pause and ask: “Exactly how to charge an AGM car battery safely and effectively?”
AGM (Absorbed Glass Mat) batteries have become incredibly popular, and for good reason. They’re more robust, resist vibration better, and offer consistent power delivery, making them a top choice for modern cars packed with electronics, start-stop systems, and even RVs or marine applications. However, their unique internal construction means they have specific charging requirements. Treat them like a conventional flooded lead-acid battery, and you could significantly shorten their lifespan, or worse, cause damage.
Don’t worry, charging an AGM battery isn’t rocket science, but it does require the right tools and a little know-how. Think of this as a friendly guide to help you keep your AGM battery in peak condition, ensuring you get the most out of your investment and avoid those frustrating moments of a car that just won’t start. We’ll walk through everything from understanding your battery to choosing the perfect charger and mastering the charging process, so you’ll confidently know how to charge an AGM car battery every time.
Key Takeaways
- Use an AGM-specific charger: Essential for safe, effective charging.
- Prioritize safety always: Ensure ventilation, wear eye protection.
- Clean battery terminals: Ensures proper connection and efficient charging.
- Connect terminals correctly: Positive first, negative to chassis last.
- Never overcharge: Use a smart charger with AGM mode for optimal results.
- Never leave charging unattended: Monitor progress for safety and optimal charging.
Quick Answers to Common Questions
What type of charger is best for an AGM car battery?
You’ll want a smart charger with an AGM mode, or one specifically designed for AGM batteries. These chargers deliver the correct voltage and current tailored for an AGM car battery, preventing damage and ensuring a full charge.
Can I use a standard lead-acid battery charger to charge an AGM car battery?
While some basic chargers might work in a pinch, it’s not ideal and can damage your battery. Standard chargers can overcharge or undercharge an AGM car battery, shortening its lifespan, so opting for an AGM-compatible charger is crucial.
How long does it typically take to charge an AGM car battery?
Charging time varies depending on the battery’s state of discharge and the charger’s amperage. A deeply discharged battery could take several hours, but a smart charger will usually indicate when the charge cycle is complete.
What’s the right voltage setting when charging an AGM car battery?
Most 12V AGM car batteries require a charging voltage between 14.4V and 14.7V. A good smart charger with an AGM setting will automatically handle this for you, taking the guesswork out of the process!
Is it possible to overcharge an AGM car battery?
Absolutely, and overcharging can significantly damage your AGM battery, reducing its capacity and lifespan. That’s why using a smart, multi-stage charger designed to safely charge an AGM car battery is highly recommended to protect your investment.
📑 Table of Contents
Understanding Your AGM Car Battery
Before we dive into the ‘how-to,’ let’s spend a moment understanding what makes AGM batteries special. Knowing their characteristics helps you appreciate why a specific charging approach is necessary.
What Makes AGM Batteries Different?
Unlike traditional flooded lead-acid batteries that have liquid electrolyte sloshing around, AGM batteries use a fine fiberglass mat saturated with electrolyte (sulfuric acid) between the battery plates. This mat absorbs the electrolyte, holding it in place. This sealed, non-spillable design is a game-changer. It means there’s no free liquid, making them maintenance-free – no need to check electrolyte levels or top them off with distilled water.
- Sealed Design: They are completely sealed, preventing leaks and spills, which is great for safety and mounting flexibility.
- Internal Recombination: During charging, oxygen and hydrogen gases are recombined internally into water, preventing gas loss and maintaining electrolyte levels.
- Low Self-Discharge: AGMs typically lose charge slower when not in use compared to conventional batteries.
Advantages of AGM Batteries
The unique construction of AGM batteries offers several compelling advantages, making them a preferred choice for many applications:
- Vibration Resistance: The tightly packed plates and absorbed electrolyte make them highly resistant to vibration, perfect for rough roads or marine use.
- Leak-Proof and Maintenance-Free: No spills, no topping off, just install and go.
- Faster Recharging: AGMs generally accept a charge faster than flooded batteries, but this efficiency requires a smart charger to prevent overcharging.
- Deep Cycle Capability: Many AGMs are designed for deep cycling, meaning they can be discharged to a lower state of charge more often without significant damage, making them excellent for auxiliary power or recreational vehicles.
The Dangers of Improper Charging
While robust, AGM batteries are sensitive to incorrect charging. This is where understanding how to charge an AGM car battery correctly becomes crucial. The biggest threat is overcharging, primarily high voltage or excessive current. Since they are sealed, gases produced during overcharging cannot escape easily. This can lead to:
- Thermal Runaway: Excessive heat builds up internally, causing a dangerous, self-accelerating cycle that can damage the battery irreversibly or even cause it to rupture.
- Reduced Lifespan: Even mild overcharging can degrade the plates and dry out the electrolyte, significantly shortening the battery’s service life.
- Permanent Damage: Swelling of the battery case, reduced capacity, and complete failure are all possible outcomes of improper charging.
The Right Tools for the Job: Choosing an AGM Battery Charger
So, you know your AGM battery is special. This means you can’t just grab any old charger from your garage. The key to knowing how to charge an AGM car battery correctly lies in selecting the right charger.
Visual guide about agm car battery charge
Image source: s3.amazonaws.com
Why a Standard Charger Won’t Cut It
Traditional lead-acid battery chargers often provide a constant, high voltage or lack sophisticated charging stages. This is problematic for AGMs:
- Voltage Profile Differences: AGMs typically require a slightly lower ‘absorption’ voltage than flooded batteries to prevent overcharging. A standard charger might push too much voltage, leading to the dangers we just discussed.
- Overcharging Risk: Without proper voltage regulation and a ‘float’ stage, a standard charger will continue to push current into an already full AGM battery, leading to damage.
Key Features to Look For
When buying a charger specifically for your AGM battery, keep an eye out for these essential features:
- “AGM Mode” or “AGM Setting”: This is non-negotiable. An AGM-specific mode ensures the charger applies the correct voltage profile and current limits for your battery type. This is the single most important factor for knowing how to charge an AGM car battery safely.
- Multi-Stage Charging: Look for chargers that employ a multi-stage charging process (usually 3 or 4 stages: bulk, absorption, float, and sometimes desulfation). This optimizes the charge, ensuring it’s efficient and safe.
- Temperature Compensation: Some advanced chargers have a temperature sensor. This allows the charger to adjust its voltage output based on ambient temperature, preventing overcharging in hot conditions and ensuring a full charge in cold conditions. This is a huge plus for battery longevity.
- Automatic Shut-off/Maintainer Function: A good AGM charger will automatically switch to a lower ‘float’ voltage once the battery is full, preventing overcharging and allowing it to be connected for extended periods (like over winter).
- Amperage Rating: As a general rule of thumb, the charger’s output current (in amps) should be approximately 10-20% of your battery’s Ah (Amp-hour) capacity. For example, a 100 Ah AGM battery could use a 10-20 amp charger. Too high an amperage can stress the battery; too low will take an extremely long time.
Types of Chargers
- Smart Chargers/Multi-Stage Chargers: These are ideal. They detect the battery’s state of charge and adjust the voltage and current through different stages. They are the best choice for charging a deeply discharged AGM battery or for regular maintenance.
- Battery Tenders/Maintainers: These are low-amperage smart chargers specifically designed for long-term connection. They keep the battery topped off at an optimal float voltage, preventing self-discharge. Perfect for vehicles stored for extended periods.
- Jump Starters (with charging function): While some jump starters have a charging capability, they are often designed for quick boosts, not comprehensive charging. Always check if they have an AGM mode and multi-stage charging before relying on them for a full charge.
Step-by-Step Guide to Charging Your AGM Car Battery
Now that you have the right equipment, let’s get hands-on. Knowing how to charge an AGM car battery involves a methodical approach, with safety as the top priority.
Visual guide about agm car battery charge
Image source: i.pinimg.com
Safety First!
Battery charging involves electricity and potentially explosive gases (though less so with sealed AGMs, caution is still paramount). Always take these precautions:
- Wear Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Safety glasses and gloves are a must.
- Ventilation: Charge in a well-ventilated area to dissipate any potential gases.
- No Sparks: Avoid open flames, smoking, or creating sparks near the battery.
- Read Your Charger’s Manual: Every charger is slightly different. Familiarize yourself with its specific instructions and safety warnings.
Preparing Your Battery
A little prep goes a long way for knowing how to charge an AGM car battery effectively.
- Locate Your Battery: If it’s in the engine bay, ensure the area is clean and accessible. Some car batteries are in the trunk or under a seat.
- Inspect for Damage: Look for cracks, leaks, or swelling in the battery case. If you see any, do NOT attempt to charge it. It’s time for a replacement.
- Clean Terminals: Ensure the battery terminals are free of dirt, corrosion, or debris. Use a wire brush if necessary. Clean terminals ensure good electrical contact for efficient charging.
Connecting the Charger
The order of connection is crucial to prevent sparks.
- Ensure Charger is OFF and UNPLUGGED: Before making any connections to the battery, make sure your charger is turned off and unplugged from the AC outlet.
- Connect Positive (Red) Clamp: Attach the red (positive, +) clamp from the charger to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Connect Negative (Black) Clamp: Attach the black (negative, -) clamp from the charger to the negative (-) terminal of the battery. If the battery is still in the vehicle, some manufacturers recommend connecting the negative clamp to a ground point on the engine block or chassis, away from the battery, to minimize spark risk near the battery’s gas vents.
- Plug in the Charger: Once both clamps are securely connected, plug the charger into a wall outlet.
Setting the Charger
This is where your AGM-specific charger comes in handy.
- Select “AGM Mode”: If your charger has an AGM setting, select it now. This tells the charger to use the appropriate voltage profile for your battery.
- Select Voltage (if applicable): Ensure you select the correct voltage (e.g., 12V for a car battery).
- Start Charging: Turn on the charger. It should begin its charging cycle, often indicated by lights or a display.
Monitoring the Charging Process
While smart chargers are mostly autonomous, it’s wise to keep an eye on things, especially if you’re new to this. Check on the battery periodically.
- Charger Indicators: Observe the charger’s indicator lights or display. They usually show the charging stage (bulk, absorption, float) and the battery’s state of charge.
- Battery Temperature: Touch the battery periodically (carefully, with gloves). It should remain cool to slightly warm. If it gets hot, something is wrong. Immediately disconnect the charger and investigate.
- Charging Time: How long to charge an AGM car battery depends on its size and how discharged it is. A deeply discharged battery could take several hours, even overnight, with a smaller charger. A fully discharged 100Ah AGM battery might take 5-10 hours with a 10-20A charger.
Disconnecting After Charging
Just as with connecting, the disconnection order is important to prevent sparks.
- Turn OFF and UNPLUG Charger: First, turn off the charger and then unplug it from the AC outlet.
- Disconnect Negative (Black) Clamp: Remove the black (negative, -) clamp from the battery terminal (or chassis ground).
- Disconnect Positive (Red) Clamp: Remove the red (positive, +) clamp from the positive (+) battery terminal.
You’ve successfully learned how to charge an AGM car battery!
Optimal Charging Practices for Longevity
Knowing how to charge an AGM car battery goes beyond just connecting the clamps; it’s about adopting practices that maximize its lifespan and performance.
The Importance of Multi-Stage Charging
Modern smart chargers are designed to go through several stages, each optimized for a specific part of the charging process:
- Bulk Stage: This is where the charger delivers maximum current to rapidly bring the battery to about 80% state of charge. Voltage increases during this stage.
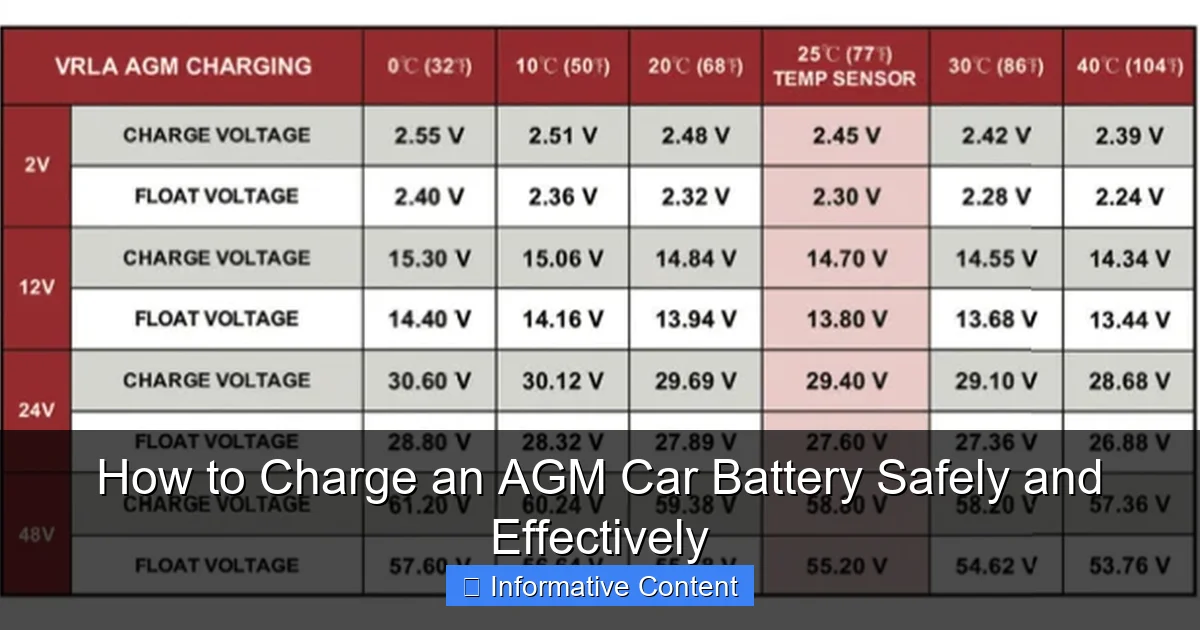
- Absorption Stage: Once the battery reaches about 80%, the charger holds a constant, slightly lower voltage (typically 14.4-14.7V for 12V AGM batteries) while the current gradually decreases. This carefully brings the battery to 100% charge without overstressing it. This is a critical stage for knowing how to charge an AGM car battery without damage.
- Float Stage: Once the battery is fully charged, the charger reduces the voltage to a lower “float” level (around 13.4-13.8V for 12V AGM batteries). This maintains the battery at full charge, compensating for self-discharge, without overcharging. It’s like a gentle top-up.
- Desulfation (Optional): Some advanced chargers have a desulfation mode, which uses pulses of voltage to break down sulfate crystals that can form on battery plates, especially in deeply discharged batteries. This can sometimes revive a neglected battery.
Avoiding Overcharging and Undercharging
Both extremes are detrimental to your AGM battery:
- Overcharging: As discussed, too much voltage or current, especially in the absorption or float stages, leads to gasification, water loss, and heat, damaging the battery and reducing its life. This is why an AGM-specific charger is vital.
- Undercharging: Consistently not fully charging an AGM battery can lead to sulfation – the buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the plates. This reduces the battery’s capacity and ability to hold a charge over time. Many short trips where the alternator doesn’t have enough time to fully recharge the battery can lead to chronic undercharging.
When to Use a Battery Maintainer
A battery maintainer (often a smart charger with a dedicated float stage) is your AGM battery’s best friend for periods of inactivity. If you have a car, motorcycle, RV, or boat that sits for weeks or months, connect it to an AGM-compatible battery maintainer. It will keep the battery at an optimal float voltage, preventing self-discharge and ensuring it’s always ready to go. This is a crucial part of knowing how to charge an AGM car battery for long-term storage.
Temperature’s Role in Charging
Battery performance and charging requirements are affected by temperature:
- Cold Temperatures: In cold weather, batteries accept a charge less efficiently, and their capacity temporarily decreases. A smart charger with temperature compensation can slightly increase the charging voltage to ensure a full charge.
- Hot Temperatures: In hot weather, batteries are more susceptible to overcharging. A temperature-compensated charger will reduce the charging voltage to prevent thermal runaway.
Always charge your battery in a moderately temperate, well-ventilated area if possible.
Troubleshooting Common Charging Issues
Even with the right knowledge on how to charge an AGM car battery, sometimes things don’t go as planned. Here are some common issues and what to do.
Battery Not Accepting a Charge
If your charger indicates an error or the battery isn’t taking a charge:
- Deep Discharge: An AGM battery that has been left completely flat for an extended period might have entered a deep discharge state, where its voltage is too low for a standard smart charger to “wake up” and begin charging. Some advanced chargers have a “repair” or “desulfation” mode that can sometimes recover these batteries by applying controlled pulses. If not, the battery might be permanently damaged.
- Sulfation: As mentioned, persistent undercharging can lead to sulfation, making it harder for the battery to accept and hold a charge. Desulfation mode on some chargers might help.
- Internal Damage: If the battery is old or has been severely abused (e.g., from repeated deep discharges or overcharging), it might have internal damage preventing it from taking a charge.
Charger Indicator Lights Not Behaving
If your charger is showing unusual lights or error codes:
- Check Connections: Double-check that all positive and negative clamps are securely connected to the correct terminals. A loose connection can prevent charging.
- Faulty Charger: Try testing your charger on another known-good battery (if available) to rule out a charger malfunction.
- Internal Battery Short: If the charger immediately goes into an error state or shows a fully charged light on a clearly dead battery, it could indicate an internal short circuit within the battery. This means the battery is likely beyond repair.
Battery Getting Hot During Charging
This is a serious warning sign and indicates a problem.
- Immediately Disconnect: If the battery becomes hot to the touch during charging, immediately disconnect the charger.
- Overcharging: The most common cause is overcharging, especially if you’re not using an AGM-specific charger or if the charger’s AGM mode isn’t working correctly.
- Internal Damage: Heat can also indicate internal battery damage or a short, which causes excessive resistance and heat buildup. Do not attempt to recharge a hot battery. It’s likely time for a replacement.
When to Consider Battery Replacement
Even with perfect charging, batteries don’t last forever. Consider replacement if:
- Age: Most AGM car batteries have a lifespan of 3-7 years, depending on usage and climate.
- Persistent Issues: If it repeatedly struggles to hold a charge, requires frequent jump starts, or shows signs of swelling or leakage, it’s time for a new one.
- Testing Failure: A professional battery test (load test) can determine its remaining capacity and health. If it fails a load test, it’s time to replace it.
AGM Battery Voltage and State of Charge
Understanding battery voltage is key to monitoring its health and charge status. Here’s a quick reference:
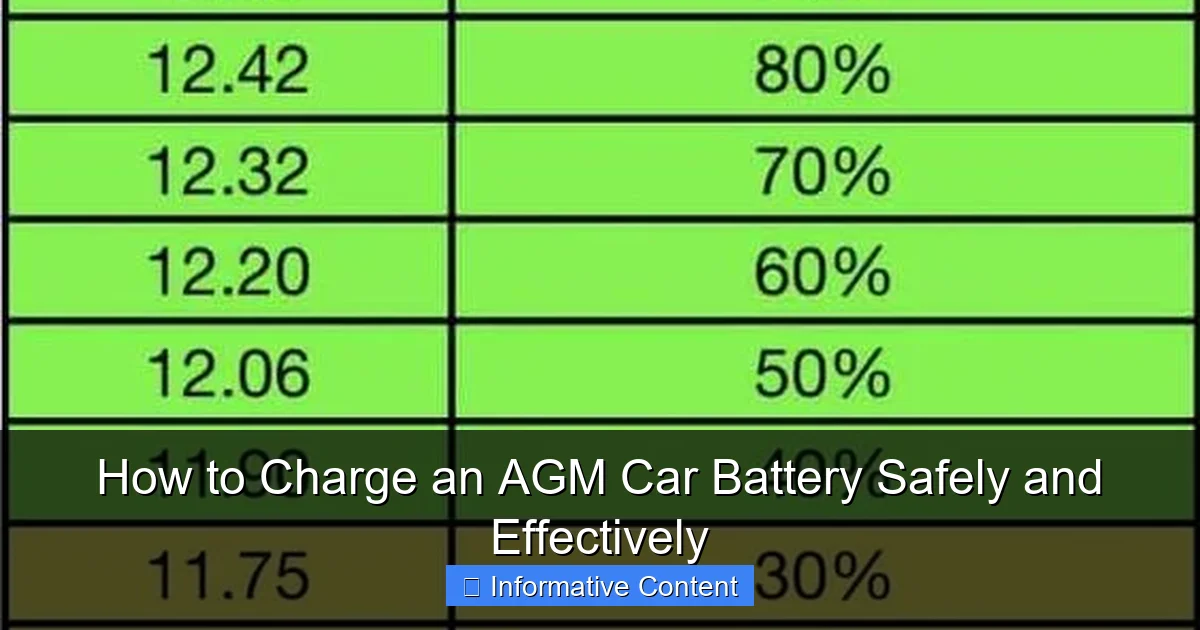
Here’s a handy table to help you understand the state of charge for a 12V AGM battery based on its resting voltage (after being at rest for at least 12-24 hours without charge or discharge).
| Voltage (12V Battery) | Approximate State of Charge (%) | Condition |
|---|---|---|
| 12.8V – 12.9V | 100% | Fully Charged |
| 12.5V – 12.6V | 75% | Good Charge |
| 12.2V – 12.3V | 50% | Half Charged (Recharge Soon) |
| 12.0V – 12.1V | 25% | Low Charge (Recharge Immediately) |
| < 12.0V | Discharged | Very Low / Deeply Discharged |
Remember, these are resting voltages. A battery under load will show a lower voltage.
For charger amperage, a simple guide:
| Battery Capacity (Ah) | Recommended Charger Amperage (A) |
|---|---|
| 20 Ah | 2-4 A |
| 50 Ah | 5-10 A |
| 80 Ah | 8-16 A |
| 100 Ah | 10-20 A |
| 120 Ah | 12-24 A |
This table provides a rough guideline. Always refer to your battery manufacturer’s recommendations for precise charging parameters.
Conclusion
Charging your AGM car battery doesn’t have to be a source of anxiety. By understanding what makes these batteries unique, investing in the right charger with an “AGM mode,” and following a few simple safety and procedural steps, you’ll be well on your way to maximizing your battery’s life and ensuring reliable power for your vehicle.
Remember, the golden rule for how to charge an AGM car battery is to use an AGM-specific, multi-stage smart charger. This small investment will pay dividends in preventing costly damage and extending the life of your battery. Always prioritize safety, read your manuals, and when in doubt, consult a professional. With this knowledge, you can confidently keep your AGM battery healthy, ready to power your adventures for years to come.
🎥 Related Video: How to Charge and Test Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) Batteries
📺 Delphi
For more information on Delphi Technologies MaxStart Batteries, visit our website!
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of charger is best for an AGM car battery?
To charge an AGM car battery safely and effectively, you should always use a smart charger designed specifically for AGM batteries. These multi-stage chargers automatically adjust voltage and amperage throughout the charging cycle, preventing overcharging and damage while optimizing battery life. Look for one with a dedicated “AGM” mode.
Can I use a standard car battery charger to charge an AGM car battery?
It depends on the charger. While many modern “standard” smart chargers now include an AGM mode, older or basic trickle chargers are generally not suitable. Using a non-AGM compatible charger can lead to overcharging, overheating, and significantly shorten the lifespan of your AGM car battery due to their unique charging requirements.
How long does it take to fully charge an AGM car battery?
The charging time for an AGM car battery varies based on its size (Ah rating), current state of discharge, and the output current of your charger. A moderately discharged battery might take 4-12 hours, while a deeply discharged battery could require 12-24 hours or more for a full charge. Always monitor your charger’s indicators for completion.
What is the recommended voltage and amperage for charging an AGM car battery?
Most AGM car batteries require an absorption voltage between 14.4V and 14.7V, followed by a float voltage of 13.5V to 13.8V once fully charged. The charging amperage should generally be between 10% and 25% of the battery’s Ah (Amp-hour) rating. Smart chargers designed for AGM batteries automatically manage these parameters for optimal charging.
Is it possible to overcharge or damage an AGM car battery?
Yes, AGM car batteries are sensitive to overcharging, which can cause internal damage, reduce their capacity, and shorten their lifespan. Using the wrong type of charger, or leaving a non-smart charger connected for too long, can lead to excessive heat, gassing, and permanent damage to the battery’s internal structure.
What are the safety precautions when charging an AGM car battery?
Always ensure you are charging in a well-ventilated area, wear safety glasses, and remove any metal jewelry to prevent short circuits. Connect the positive (+) charger clamp to the positive battery terminal and the negative (-) clamp to the negative terminal (or a grounded point on the vehicle chassis away from the battery), then plug in the charger last.